biweekly-contest-35
A
Statement
Metadata
- Link: 所有奇数长度子数组的和
- Difficulty: Easy
- Tag:
数组数学前缀和
给你一个正整数数组 arr ,请你计算所有可能的奇数长度子数组的和。
子数组 定义为原数组中的一个连续子序列。
请你返回 arr 中 所有奇数长度子数组的和 。
示例 1:
输入:arr = [1,4,2,5,3]
输出:58
解释:所有奇数长度子数组和它们的和为:
[1] = 1
[4] = 4
[2] = 2
[5] = 5
[3] = 3
[1,4,2] = 7
[4,2,5] = 11
[2,5,3] = 10
[1,4,2,5,3] = 15
我们将所有值求和得到 1 + 4 + 2 + 5 + 3 + 7 + 11 + 10 + 15 = 58示例 2:
输入:arr = [1,2]
输出:3
解释:总共只有 2 个长度为奇数的子数组,[1] 和 [2]。它们的和为 3 。示例 3:
输入:arr = [10,11,12]
输出:66
提示:
1 <= arr.length <= 1001 <= arr[i] <= 1000
Metadata
- Link: Sum of All Odd Length Subarrays
- Difficulty: Easy
- Tag:
ArrayMathPrefix Sum
Given an array of positive integers arr, calculate the sum of all possible odd-length subarrays.
A subarray is a contiguous subsequence of the array.
Return the sum of all odd-length subarrays of arr.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [1,4,2,5,3]
Output: 58
Explanation: The odd-length subarrays of arr and their sums are:
[1] = 1
[4] = 4
[2] = 2
[5] = 5
[3] = 3
[1,4,2] = 7
[4,2,5] = 11
[2,5,3] = 10
[1,4,2,5,3] = 15
If we add all these together we get 1 + 4 + 2 + 5 + 3 + 7 + 11 + 10 + 15 = 58Example 2:
Input: arr = [1,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: There are only 2 subarrays of odd length, [1] and [2]. Their sum is 3.Example 3:
Input: arr = [10,11,12]
Output: 66
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 1001 <= arr[i] <= 1000
Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl "\n"
#define fi first
#define se second
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define mkp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
using db = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
using pII = pair<int, int>;
using pLL = pair<ll, ll>;
constexpr int mod = 1e9 + 7;
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chadd(T1 &x, T2 y, int Mod = mod) {
x += y;
while (x >= Mod) x -= Mod;
while (x < 0) x += Mod;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmax(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x < y)
x = y;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmin(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x > y)
x = y;
}
inline int nextInt() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
void rd() {}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void rd(T &arg, Ts &...args) {
cin >> arg;
rd(args...);
}
#define dbg(x...) \
do { \
cout << "\033[32;1m" << #x << " -> "; \
err(x); \
} while (0)
void err() {
cout << "\033[39;0m" << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void err(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg << ' ';
err(args...);
}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (auto &v : arg) cout << v << ' ';
err(args...);
}
void ptt() {
cout << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void ptt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << ' ' << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void pt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
void pt() {}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void pt(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (int i = 0, sze = arg.size(); i < sze; ++i) cout << arg[i] << " \n"[i == sze - 1];
pt(args...);
}
inline ll qpow(ll base, ll n) {
assert(n >= 0);
ll res = 1;
while (n) {
if (n & 1)
res = res * base % mod;
base = base * base % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
// head
constexpr int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, sum[N];
class Solution {
public:
int sumOddLengthSubarrays(vector<int> &arr) {
n = SZ(arr);
int res = 0;
sum[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) sum[i + 1] = sum[i] + arr[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
if ((j - i + 1) & 1) {
res += sum[j + 1] - sum[i];
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
#ifdef LOCAL
int main() {
return 0;
}
#endif
B
Statement
Metadata
- Link: 所有排列中的最大和
- Difficulty: Medium
- Tag:
贪心数组前缀和排序
有一个整数数组 nums ,和一个查询数组 requests ,其中 requests[i] = [starti, endi] 。第 i 个查询求 nums[starti] + nums[starti + 1] + … + nums[endi - 1] + nums[endi] 的结果 ,starti 和 endi 数组索引都是 从 0 开始 的。
你可以任意排列 nums 中的数字,请你返回所有查询结果之和的最大值。
由于答案可能会很大,请你将它对 109 + 7 取余 后返回。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4,5], requests = [[1,3],[0,1]]
输出:19
解释:一个可行的 nums 排列为 [2,1,3,4,5],并有如下结果:
requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 1 + 3 + 4 = 8
requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 1 = 3
总和为:8 + 3 = 11。
一个总和更大的排列为 [3,5,4,2,1],并有如下结果:
requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 5 + 4 + 2 = 11
requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 3 + 5 = 8
总和为: 11 + 8 = 19,这个方案是所有排列中查询之和最大的结果。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6], requests = [[0,1]]
输出:11
解释:一个总和最大的排列为 [6,5,4,3,2,1] ,查询和为 [11]。示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4,5,10], requests = [[0,2],[1,3],[1,1]]
输出:47
解释:一个和最大的排列为 [4,10,5,3,2,1] ,查询结果分别为 [19,18,10]。
提示:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 1051 <= requests.length <= 105requests[i].length == 20 <= starti <= endi < n
Metadata
- Link: Maximum Sum Obtained of Any Permutation
- Difficulty: Medium
- Tag:
GreedyArrayPrefix SumSorting
We have an array of integers, nums, and an array of requests where requests[i] = [starti, endi]. The ith request asks for the sum of nums[starti] + nums[starti + 1] + … + nums[endi - 1] + nums[endi]. Both starti and endi are 0-indexed.
Return the maximum total sum of all requests among all permutations of nums.
Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5], requests = [[1,3],[0,1]]
Output: 19
Explanation: One permutation of nums is [2,1,3,4,5] with the following result:
requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 1 + 3 + 4 = 8
requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 1 = 3
Total sum: 8 + 3 = 11.
A permutation with a higher total sum is [3,5,4,2,1] with the following result:
requests[0] -> nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[3] = 5 + 4 + 2 = 11
requests[1] -> nums[0] + nums[1] = 3 + 5 = 8
Total sum: 11 + 8 = 19, which is the best that you can do.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6], requests = [[0,1]]
Output: 11
Explanation: A permutation with the max total sum is [6,5,4,3,2,1] with request sums [11].Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,10], requests = [[0,2],[1,3],[1,1]]
Output: 47
Explanation: A permutation with the max total sum is [4,10,5,3,2,1] with request sums [19,18,10].
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 1051 <= requests.length <= 105requests[i].length == 20 <= starti <= endi < n
Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl "\n"
#define fi first
#define se second
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define mkp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
using db = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
using pII = pair<int, int>;
using pLL = pair<ll, ll>;
constexpr int mod = 1e9 + 7;
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chadd(T1 &x, T2 y, int Mod = mod) {
x += y;
while (x >= Mod) x -= Mod;
while (x < 0) x += Mod;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmax(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x < y)
x = y;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmin(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x > y)
x = y;
}
inline int nextInt() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
void rd() {}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void rd(T &arg, Ts &...args) {
cin >> arg;
rd(args...);
}
#define dbg(x...) \
do { \
cout << "\033[32;1m" << #x << " -> "; \
err(x); \
} while (0)
void err() {
cout << "\033[39;0m" << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void err(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg << ' ';
err(args...);
}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (auto &v : arg) cout << v << ' ';
err(args...);
}
void ptt() {
cout << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void ptt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << ' ' << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void pt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
void pt() {}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void pt(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (int i = 0, sze = arg.size(); i < sze; ++i) cout << arg[i] << " \n"[i == sze - 1];
pt(args...);
}
inline ll qpow(ll base, ll n) {
assert(n >= 0);
ll res = 1;
while (n) {
if (n & 1)
res = res * base % mod;
base = base * base % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
// head
constexpr int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, cnt[N];
class Solution {
public:
int maxSumRangeQuery(vector<int> &nums, vector<vector<int>> &requests) {
n = SZ(nums);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cnt[i] = 0;
for (auto &it : requests) {
++it[0];
++it[1];
++cnt[it[0]];
--cnt[it[1] + 1];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
}
sort(cnt + 1, cnt + 1 + n);
sort(all(nums));
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
chadd(res, 1ll * cnt[i] * nums[i - 1] % mod);
}
return res;
}
};
#ifdef LOCAL
int main() {
return 0;
}
#endif
C
Statement
Metadata
- Link: 使数组和能被 P 整除
- Difficulty: Medium
- Tag:
数组哈希表前缀和
给你一个正整数数组 nums,请你移除 最短 子数组(可以为 空),使得剩余元素的 和 能被 p 整除。 不允许 将整个数组都移除。
请你返回你需要移除的最短子数组的长度,如果无法满足题目要求,返回 -1 。
子数组 定义为原数组中连续的一组元素。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,1,4,2], p = 6
输出:1
解释:nums 中元素和为 10,不能被 p 整除。我们可以移除子数组 [4] ,剩余元素的和为 6 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [6,3,5,2], p = 9
输出:2
解释:我们无法移除任何一个元素使得和被 9 整除,最优方案是移除子数组 [5,2] ,剩余元素为 [6,3],和为 9 。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,2,3], p = 3
输出:0
解释:和恰好为 6 ,已经能被 3 整除了。所以我们不需要移除任何元素。
示例 4:
输入:nums = [1,2,3], p = 7
输出:-1
解释:没有任何方案使得移除子数组后剩余元素的和被 7 整除。
示例 5:
输入:nums = [1000000000,1000000000,1000000000], p = 3
输出:0
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 1091 <= p <= 109
Metadata
- Link: Make Sum Divisible by P
- Difficulty: Medium
- Tag:
ArrayHash TablePrefix Sum
Given an array of positive integers nums, remove the smallest subarray (possibly empty) such that the sum of the remaining elements is divisible by p. It is not allowed to remove the whole array.
Return the length of the smallest subarray that you need to remove, or -1 if it's impossible.
A subarray is defined as a contiguous block of elements in the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,1,4,2], p = 6
Output: 1
Explanation: The sum of the elements in nums is 10, which is not divisible by 6. We can remove the subarray [4], and the sum of the remaining elements is 6, which is divisible by 6.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [6,3,5,2], p = 9
Output: 2
Explanation: We cannot remove a single element to get a sum divisible by 9. The best way is to remove the subarray [5,2], leaving us with [6,3] with sum 9.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], p = 3
Output: 0
Explanation: Here the sum is 6. which is already divisible by 3. Thus we do not need to remove anything.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 1091 <= p <= 109
Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl "\n"
#define fi first
#define se second
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define mkp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
using db = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
using pII = pair<int, int>;
using pLL = pair<ll, ll>;
constexpr int mod = 1e9 + 7;
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chadd(T1 &x, T2 y, int Mod = mod) {
x += y;
while (x >= Mod) x -= Mod;
while (x < 0) x += Mod;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmax(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x < y)
x = y;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmin(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x > y)
x = y;
}
inline int nextInt() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
void rd() {}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void rd(T &arg, Ts &...args) {
cin >> arg;
rd(args...);
}
#define dbg(x...) \
do { \
cout << "\033[32;1m" << #x << " -> "; \
err(x); \
} while (0)
void err() {
cout << "\033[39;0m" << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void err(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg << ' ';
err(args...);
}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (auto &v : arg) cout << v << ' ';
err(args...);
}
void ptt() {
cout << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void ptt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << ' ' << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void pt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
void pt() {}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void pt(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (int i = 0, sze = arg.size(); i < sze; ++i) cout << arg[i] << " \n"[i == sze - 1];
pt(args...);
}
inline ll qpow(ll base, ll n) {
assert(n >= 0);
ll res = 1;
while (n) {
if (n & 1)
res = res * base % mod;
base = base * base % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
// head
constexpr int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, sum[N];
class Solution {
public:
int minSubarray(vector<int> &nums, int p) {
n = SZ(nums);
map<int, int> mp;
int res = n + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sum[i + 1] = sum[i] + nums[i];
sum[i + 1] %= p;
}
mp[0] = 0;
int need = sum[n];
if (need == 0)
return 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int tar = (sum[i] - need + p) % p;
// need - sum[i] + p) % p;
if (mp.count(tar))
chmin(res, i - mp[tar]);
mp[sum[i]] = i;
}
if (res >= n)
res = -1;
return res;
}
};
#ifdef LOCAL
int main() {
return 0;
}
#endif
D
Statement
Metadata
- Link: 奇怪的打印机 II
- Difficulty: Hard
- Tag:
图拓扑排序数组矩阵
给你一个奇怪的打印机,它有如下两个特殊的打印规则:
- 每一次操作时,打印机会用同一种颜色打印一个矩形的形状,每次打印会覆盖矩形对应格子里原本的颜色。
- 一旦矩形根据上面的规则使用了一种颜色,那么 相同的颜色不能再被使用 。
给你一个初始没有颜色的 m x n 的矩形 targetGrid ,其中 targetGrid[row][col] 是位置 (row, col) 的颜色。
如果你能按照上述规则打印出矩形 targetGrid ,请你返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
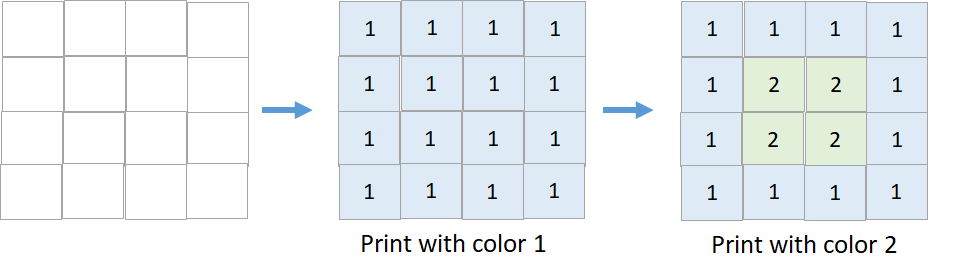
输入:targetGrid = [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,1],[1,2,2,1],[1,1,1,1]]
输出:true
示例 2:
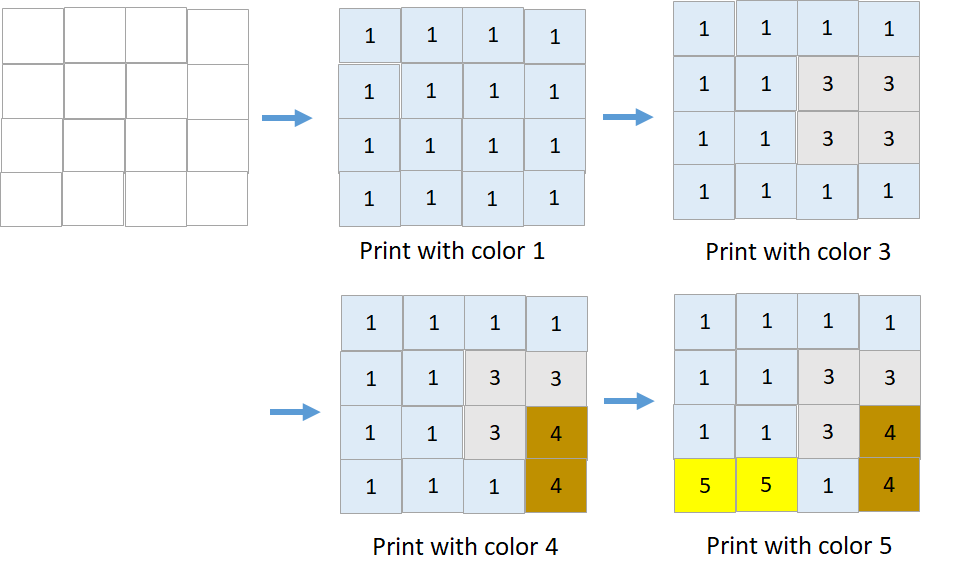
输入:targetGrid = [[1,1,1,1],[1,1,3,3],[1,1,3,4],[5,5,1,4]]
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:targetGrid = [[1,2,1],[2,1,2],[1,2,1]]
输出:false
解释:没有办法得到 targetGrid ,因为每一轮操作使用的颜色互不相同。示例 4:
输入:targetGrid = [[1,1,1],[3,1,3]]
输出:false
提示:
m == targetGrid.lengthn == targetGrid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 601 <= targetGrid[row][col] <= 60
Metadata
- Link: Strange Printer II
- Difficulty: Hard
- Tag:
GraphTopological SortArrayMatrix
There is a strange printer with the following two special requirements:
- On each turn, the printer will print a solid rectangular pattern of a single color on the grid. This will cover up the existing colors in the rectangle.
- Once the printer has used a color for the above operation, the same color cannot be used again.
You are given a m x n matrix targetGrid, where targetGrid[row][col] is the color in the position (row, col) of the grid.
Return true if it is possible to print the matrix targetGrid, otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
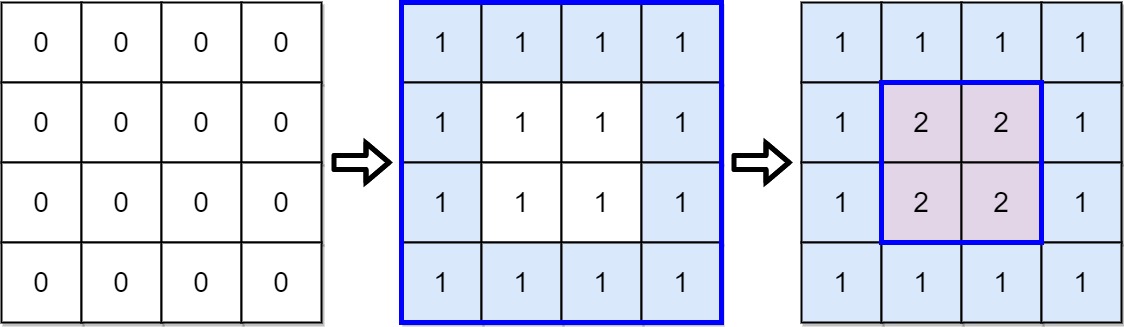
Input: targetGrid = [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,1],[1,2,2,1],[1,1,1,1]]
Output: true
Example 2:
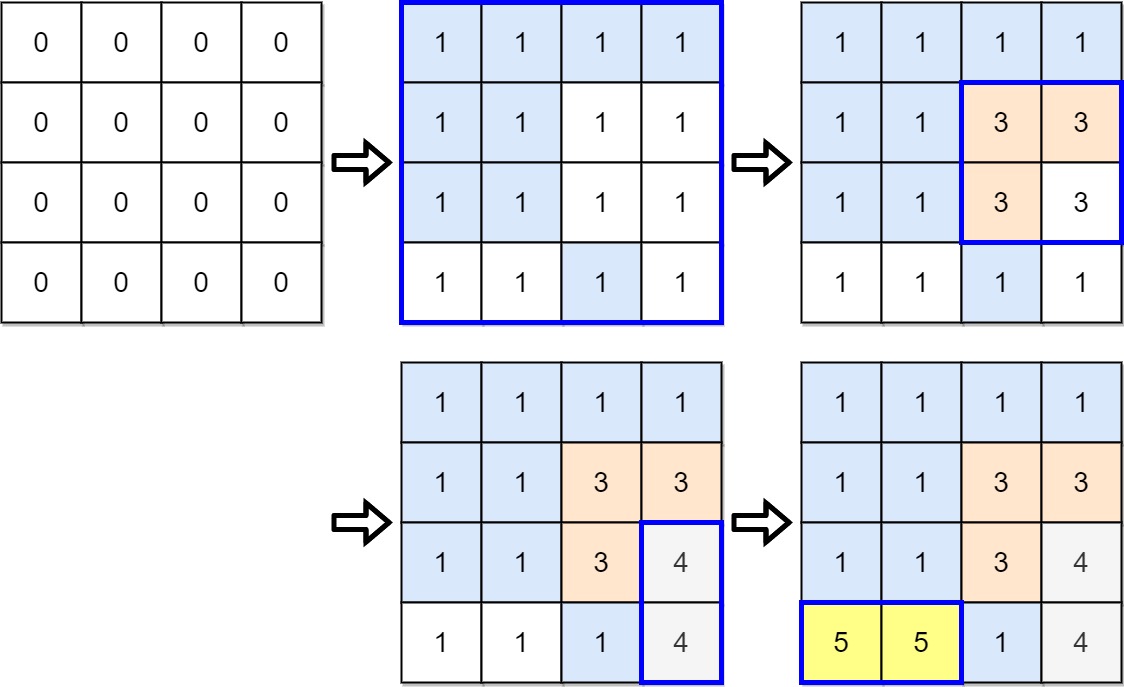
Input: targetGrid = [[1,1,1,1],[1,1,3,3],[1,1,3,4],[5,5,1,4]]
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: targetGrid = [[1,2,1],[2,1,2],[1,2,1]]
Output: false
Explanation: It is impossible to form targetGrid because it is not allowed to print the same color in different turns.
Constraints:
m == targetGrid.lengthn == targetGrid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 601 <= targetGrid[row][col] <= 60
Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl "\n"
#define fi first
#define se second
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define mkp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
using db = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
using pII = pair<int, int>;
using pLL = pair<ll, ll>;
constexpr int mod = 1e9 + 7;
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chadd(T1 &x, T2 y, int Mod = mod) {
x += y;
while (x >= Mod) x -= Mod;
while (x < 0) x += Mod;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmax(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x < y)
x = y;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void chmin(T1 &x, T2 y) {
if (x > y)
x = y;
}
inline int nextInt() {
int x;
cin >> x;
return x;
}
void rd() {}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void rd(T &arg, Ts &...args) {
cin >> arg;
rd(args...);
}
#define dbg(x...) \
do { \
cout << "\033[32;1m" << #x << " -> "; \
err(x); \
} while (0)
void err() {
cout << "\033[39;0m" << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void err(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg << ' ';
err(args...);
}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (auto &v : arg) cout << v << ' ';
err(args...);
}
void ptt() {
cout << endl;
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void ptt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << ' ' << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
template <class T, class... Ts>
void pt(const T &arg, const Ts &...args) {
cout << arg;
ptt(args...);
}
void pt() {}
template <template <typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void pt(const T<t> &arg, const A &...args) {
for (int i = 0, sze = arg.size(); i < sze; ++i) cout << arg[i] << " \n"[i == sze - 1];
pt(args...);
}
inline ll qpow(ll base, ll n) {
assert(n >= 0);
ll res = 1;
while (n) {
if (n & 1)
res = res * base % mod;
base = base * base % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
// head
constexpr int N = 1e2 + 10;
int n, m, vis[N][N];
vector<vector<int>> g;
bool valid(int x, int y) {
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m)
return false;
return true;
}
int Move[][2] = {
-1,
0,
1,
0,
0,
-1,
0,
1,
};
void dfs(int x, int y, int z) {
if (vis[x][y])
return;
vis[x][y] = 1;
// g[x][y] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int nx = x + Move[i][0];
int ny = y + Move[i][1];
if (valid(nx, ny) && (g[nx][ny] == 0 || g[nx][ny] == z)) {
dfs(nx, ny, z);
}
}
}
int calc() {
vector<int> vec(61);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
vec[g[i][j]] = 1;
}
}
vec[0] = 0;
return accumulate(all(vec), 0);
}
class Solution {
public:
bool isPrintable(vector<vector<int>> &targetGrid) {
n = SZ(targetGrid);
m = SZ(targetGrid[0]);
g = targetGrid;
int cnt = calc();
while (cnt) {
for (int i = 60; i >= 1; --i) {
int cnt = 0;
int E9 = 1e9;
int x[2] = {E9, -E9}, y[2] = {E9, -E9};
// memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
if (g[j][k] == i) {
chmin(x[0], j);
chmax(x[1], j);
chmin(y[0], k);
chmax(y[1], k);
}
}
}
bool ok = 1;
for (int j = x[0]; j <= x[1]; ++j) {
for (int k = y[0]; k <= y[1]; ++k) {
if (g[j][k] != 0 && g[j][k] != i) {
ok = 0;
}
}
}
if (ok) {
for (int j = x[0]; j <= x[1]; ++j) {
for (int k = y[0]; k <= y[1]; ++k) {
g[j][k] = 0;
}
}
}
// if (cnt == 1) {
// for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
// for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
// if (g[j][k] == i) {
// g[j][k] = 0;
// }
// }
// }
// }
}
int now = calc();
if (now == cnt)
return false;
cnt = now;
}
return true;
}
};
#ifdef LOCAL
int main() {
return 0;
}
#endif